Thermal Management and Its’ Role in “Net Zero” Emissions
In today’s environmentally progressive push, many companies across the globe are committing to a future goal of “net zero” emissions. This creates an enormous task for engineers to design solutions intended to support this initiative. Fuel cells are a popular example of “net zero” technology for generating power. This promising technology facilitates clean and efficient energy generation across a variety of applications. Fuel cell thermal management poses a significant challenge for engineers.
Importance of Thermal Management of a Fuel Cell
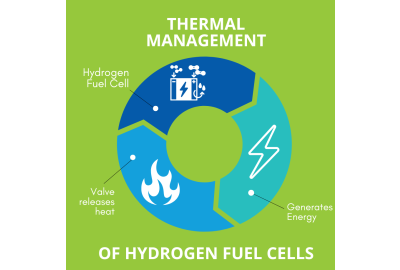
Fuel cell thermal management refers to the flow in and out of the valve controlling the cell's temperature. Thermal management directly impacts the overall performance and efficiency of a fuel cell. If the temperature becomes too hot, the cell can degrade over time. If too cold, the cell may not operate at maximum capacity. A properly regulated hydrogen fuel cell will produce maximum energy at a lower cost than an irregulated cell. Any process that moves or stores hydrogen requires a valve to regulate the flow in and out of the cell, thus controlling the temperature.
To extend the life of your hydrogen fuel cell(s) you must maintain an optimum environment for the technology to operate efficiently. This is created in part by consistent and reliable thermal management.

Exothermic Reactions Within a Fuel Cell
Many factors can affect the temperature of a fuel cell. The greatest threat to a thermal equilibrium is the exothermic reaction that occurs within the fuel cell itself. The main component of a hydrogen fuel cell is the membrane electrode assembly (MEA). The MEA is responsible for converting the chemical energy of hydrogen fuel into electrical energy. During the MEA process heat is produced as a byproduct. This heat must be strategically released to insure optimal operation temperatures. The MEA process must be conducted in a narrow temperature range, presenting the need for a temperature control valve. For example, many fuel cells used in cars need to have heat be rejected across a 40°C temperature difference. This results in the need for large radiators and air intake in comparison to that of a traditional internal combustion engine.
How does AMOT Support Thermal Management in a Fuel Cell?
A hydrogen fuel cell uses the chemical energy of hydrogen to create electric energy. Hydrogen fuel can be created using several different methods. Click here to learn more about the distinct types of hydrogen. Regardless of the creation method used or color of hydrogen, AMOT has a thermal management valve solution to optimize performance and safety.
AMOT’s extensive research and development initiatives facilitate the ability for customization specific to your application. By leveraging the benefits of accurate temperature management, your fuel cell can function at peak production, cutting excess operation costs and reducing the size and scope of other items in the cooling circuit. In addition to financial incentive, proper temperature control can increase the longevity of your fuel cell’s lifetime and create a safer working environment for employees.
Submit the form below to connect with our hydrogen experts.
Learn more about our hydrogen offerings here >>